

These higher energy atoms are then detected by sensors and through complex experimental techniques the frequency of oscillation can be determined.Ītomic clocks are one of the most accurate measures of timekeeping with an uncertainty of less than 1 second in 100 million years. The caesium atoms are bombarded with microwaves which make them transition to a higher energy state.
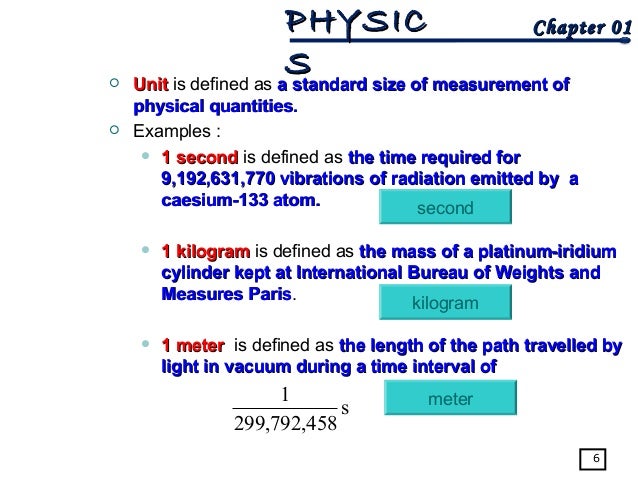
This frequency is equal to the resonant frequency of a caesium atom. Caesium was decided on as the element of choice, and the frequency of 9,192,631,770Hz (times per second) was settled on to determine the second. They settled on atoms, which are known to oscillate at a rate determined by which element it is and which are immune to manufacturing errors. Scientists were looking for an object with constant oscillations, like a pendulum in a grandfather clock or a quartz oscillator in a wristwatch, but that didn’t lose its energy over time. This comes from the world’s most precise method of keeping time: atomic clocks.Ītomic clocks are a relatively new invention, dating back to just 1948 when the first one was made, and later in 1955 when the first caesium atomic clock was made. If you google the definition of a second, you might be surprised to read that rather than it being defined by the earth’s rotation and subsequent hours and minutes, it is determined as the amount of time it takes a caesium-133 atom to oscillate 9,192,631,770 times.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
